In the world of computer hardware, certain components often steal the spotlight. Graphic cards, processors, and storage drives are all essential pieces that captivate the attention of tech enthusiasts. However, there’s a silent hero lurking within your PC’s case, quietly performing a crucial role in the background—the Power Supply Unit (PSU). This article will shed light on the often-underappreciated functions of a Power Supply Unit (PSU) in your PC, emphasizing why selecting the right one is a pivotal decision for any computer enthusiast. We’ll also provide you with a comprehensive buying guide to help you make an informed choice.
Table of Contents
ToggleProviding Electrical Power
At its core, a Power Supply Unit (PSU) is the heart of your PC’s power infrastructure. Its fundamental function is to convert the electrical energy supplied from your wall outlet into a form that your computer’s internal components can utilize. This transformation process is essential because household electricity is not suitable for direct consumption by sensitive computer hardware. The PSU ensures a steady and consistent supply of power, effectively acting as a translator between your home’s electrical grid and your PC.
Distributing Power to Components
Once electricity is converted, the PSU’s next task is to distribute power effectively and efficiently to various components within your PC. This includes the motherboard, CPU, graphics card, storage drives, RAM modules, and an array of peripheral devices. Each component has distinct power requirements, and it’s the PSU’s responsibility to ensure that each one receives the appropriate amount of power to function optimally.
Protecting Against Overloads and Short Circuits
Beyond its primary role as a power provider, a well-designed PSU incorporates essential protective features. These include overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, and short-circuit protection. These safeguards act as the PC’s defense mechanism against potential risks, such as power spikes, voltage fluctuations, or hardware malfunctions. By swiftly responding to these threats, the PSU helps safeguard your computer’s components from damage, ultimately prolonging their lifespan and saving you from costly repairs.
Efficiency and Energy Conservation
In the ever-evolving landscape of PC hardware, modern PSUs come with efficiency ratings known as 80 PLUS certifications. These certifications denote how effectively the PSU converts input power into usable energy for your computer. Opting for an efficient PSU not only translates to lower energy consumption but also leads to reduced heat generation. This, in turn, contributes to a cooler and quieter PC, enhancing both your computing experience and environmental impact.
Here are some common PSU efficiency ratings and what they mean:
80 PLUS Certification
The 80 PLUS certification program is a widely recognized standard for PSU efficiency. It includes several levels of efficiency ratings, which are as follows:
- 80 PLUS: This is the basic certification, and it ensures that the PSU is at least 80% efficient at 20%, 50%, and 100% load.
- 80 PLUS Bronze: Bronze-certified PSUs are at least 82% efficient at 20%, 85% efficient at 50%, and 82% efficient at 100% load.
- 80 PLUS Silver: Silver-certified PSUs are at least 85% efficient at 20%, 88% efficient at 50%, and 85% efficient at 100% load.
- 80 PLUS Gold: Gold-certified PSUs are at least 87% efficient at 20%, 90% efficient at 50%, and 87% efficient at 100% load.
- 80 PLUS Platinum: Platinum-certified PSUs are at least 90% efficient at 20%, 92% efficient at 50%, and 89% efficient at 100% load.
- 80 PLUS Titanium: Titanium-certified PSUs are the most efficient, with a minimum efficiency of 90% at 10%, 92% at 20%, 94% at 50%, and 90% at 100% load.

Cybenetics Certification
The Cybenetics certification is an alternative to the 80 PLUS certification and provides additional information about the PSU’s noise level and efficiency. It uses the ETA (efficiency) and LAMBDA (noise) scales to rate
PSU’s Efficiency Curve
It’s important to note that PSU efficiency is not constant across all loads. Most PSUs are most efficient in a specific load range, often around 50% of their rated capacity. Efficiency tends to drop at very low and very high loads.
Choosing a PSU with an appropriate efficiency rating for your needs can save you money on electricity bills and help your computer components run more efficiently. However, it’s also important to consider the wattage and quality of the PSU, as well as any specific requirements for your components, when selecting the right power supply for your PC build.
Compatibility and Expansion
Selecting the right PSU extends beyond wattage considerations; it also involves compatibility with your current and future hardware needs. Your PSU should have adequate wattage and the appropriate connectors to support your existing components. Moreover, if you have plans to expand your system by adding more demanding components, such as additional graphics cards or storage drives, investing in a PSU with the necessary capacity is essential. This foresight can save you from future headaches when upgrading your PC.
Noise Reduction
PC enthusiasts are no strangers to the constant battle against noise pollution within their computing environments. The PSU plays a significant role in mitigating this issue. A quality PSU incorporates a fan that dynamically adjusts its speed based on temperature, leading to a quieter system. During idle or less demanding tasks, the fan operates at a lower speed, significantly reducing noise. However, when your PC is under heavy load, the fan increases its RPM to ensure effective cooling. This intelligent fan management maintains a quieter and more pleasant computing experience.
Buying Guide for Choosing the Right PSU
Now that we’ve explored the functions of a Power Supply Unit (PSU) in your PC, let’s delve into the essential considerations when purchasing one:
Wattage
Determine your PC’s power requirements. A wattage calculator can help you estimate the PSU capacity you need. It’s advisable to choose a PSU with some headroom for future upgrades.
Efficiency Rating
Look for PSUs with 80 PLUS certifications, which indicate their efficiency levels. Higher-rated PSUs not only save energy but also generate less heat.
Modularity
Consider modular or semi-modular PSUs for cleaner cable management. These PSUs allow you to attach only the cables you need, reducing clutter inside your case.
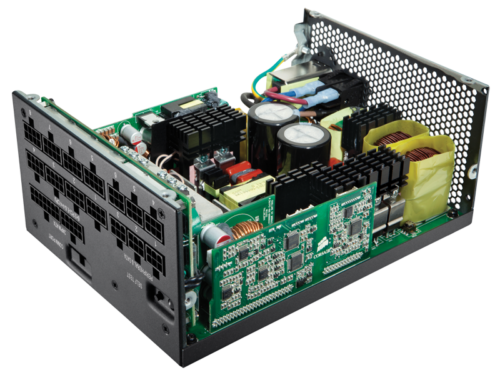
Form Factor
Ensure the PSU fits your case. Standard ATX PSUs fit most cases, but smaller cases may require SFX or TFX form factor PSUs. Form factors to consider:
- ATX (Advanced Technology Extended):
- ATX is the most widely used and standardized form factor for power supplies and computer cases.
- Dimensions: 150mm (width) x 86mm (height) x 140mm (depth).
- ATX power supplies are compatible with standard ATX and microATX cases.
- MicroATX (uATX):
- MicroATX power supplies are smaller than standard ATX power supplies.
- Dimensions: 150mm (width) x 75mm (height) x 140mm (depth).
- These power supplies are designed for smaller microATX and Mini-ITX cases.
- SFX (Small Form Factor):
- SFX power supplies are compact and designed for small form factor (SFF) cases.
- Dimensions: 125mm (width) x 63.5mm (height) x 100mm (depth).
- SFX-L (SFX-Large) power supplies are slightly larger for improved cooling.
- Suitable for Mini-ITX and some compact ATX cases.
- TFX (Thin Form Factor):
- TFX power supplies are even smaller and thinner than SFX power supplies.
- Dimensions: 85.6mm (width) x 65.1mm (height) x 175.3mm (depth).
- Commonly used in slim desktop cases and compact enclosures.
Connectors
Check that the PSU has the required connectors for your components, including graphics cards, storage drives, and CPU power.
Here are some of the most common PSU connectors:
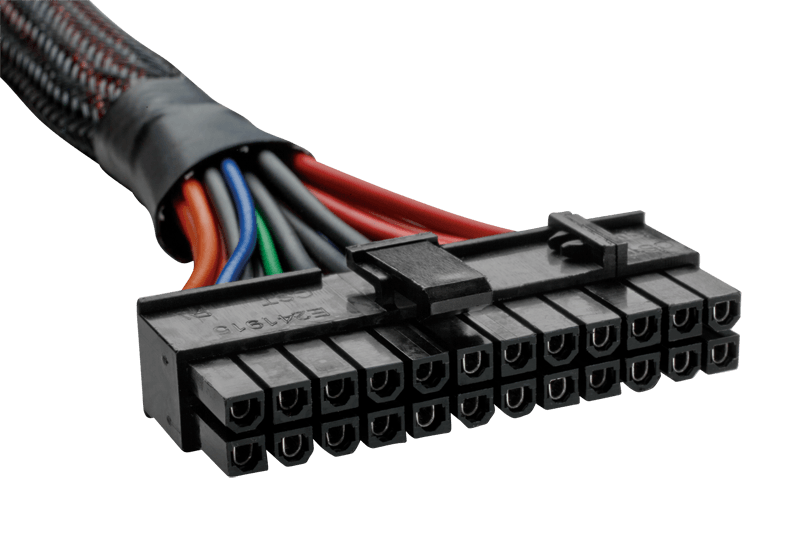
- 24-Pin ATX Connector: This large connector provides power to the motherboard and is a standard component of every PSU. It typically splits into a 20-pin and a 4-pin section for compatibility with older motherboards.
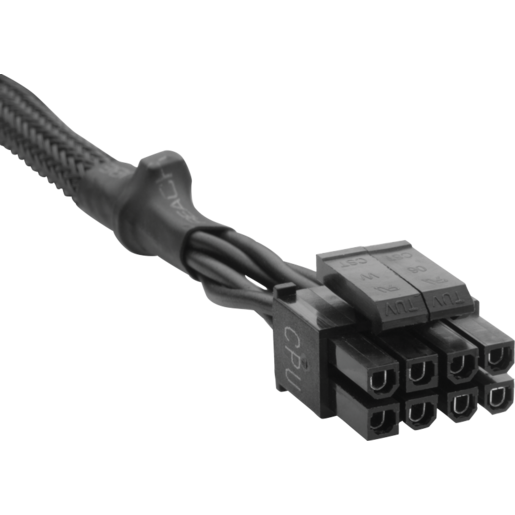
- 4-Pin/8-Pin CPU Connector (EPS/ATX12V): This connector delivers power to the CPU. Modern high-end motherboards often require an 8-pin CPU connector, while older or lower-end boards may use a 4-pin connector.
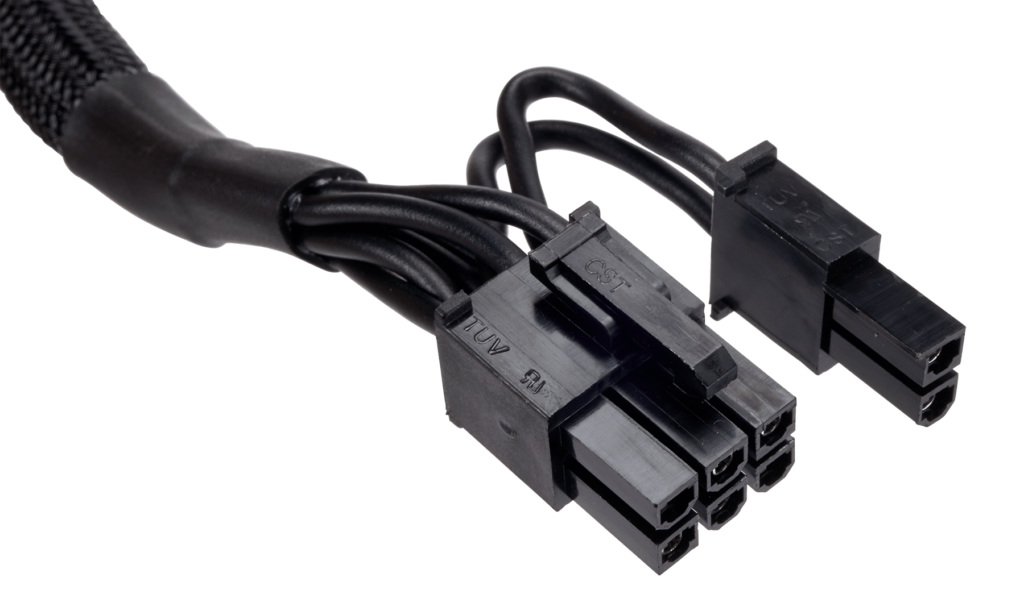
- 6-Pin and 8-Pin PCIe Connectors: These connectors supply power to graphics cards (GPUs). Some GPUs require one or more 6-pin or 8-pin connectors, depending on their power requirements.
- SATA Connectors: These flat, L-shaped connectors are used for powering SATA drives, including SSDs and HDDs. They are often found in multiples on a single cable.
- RGB and Fan Connectors: Some power supplies come with connectors for RGB lighting or fan control. These connectors can vary depending on the PSU model and manufacturer.
It’s essential to ensure that your PSU provides the necessary connectors for all your components. When building or upgrading a PC, check the power requirements of your components and make sure you have the right cables and connectors to supply power to each one. Additionally, consider cable management to keep your build neat and organized.
Brand and Quality
Stick to reputable PSU brands known for reliability and performance. Read reviews and seek recommendations from trusted sources.
Budget
Set a reasonable budget for your PSU, balancing quality and features. Don’t compromise on quality to save a few dollars.
Warranty
Choose a PSU with a decent warranty period, ideally three years or longer. A longer warranty reflects the manufacturer’s confidence in their product’s durability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the functions of a power supply unit are often underestimated. These functions encompass providing stable electrical power, distributing power efficiently, protecting against potential hazards, promoting energy efficiency, ensuring compatibility with current and future hardware, and reducing noise pollution. Selecting the right PSU tailored to your PC’s unique requirements is a decision that should not be taken lightly.
By following our comprehensive buying guide, you can confidently choose a PSU that not only meets your current needs but also accommodates future upgrades. Your PSU may operate quietly in the background, but its significance in the overall performance and longevity of your PC cannot be overstated. Make an informed choice and enjoy a stable and reliable computing experience for years to come.